<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width">
<title>JS Bin</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li> A </li>
<li> B </li>
<li> C </li>
<li> D </li>
</ul>
</body>
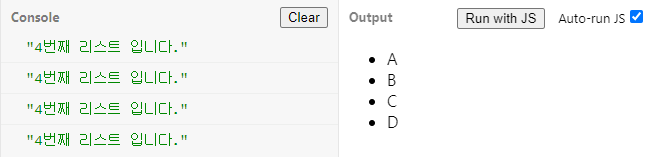
</html>var list = document.querySelectorAll("li");
for(var i=0; i<list.length; i++){
list[i].addEventListener("click" , function(){
console.log(i + "번째 리스트 입니다.")
});
}결과
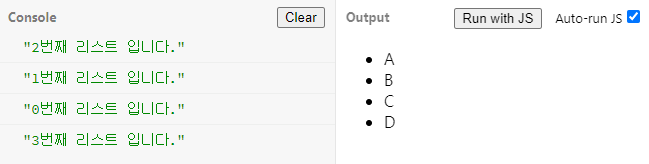
클로져 스코프 문제를 let을 통해 해결한다.
var list = document.querySelectorAll("li");
for(let i=0; i<list.length; i++){
list[i].addEventListener("click" , function(){
console.log(i + "번째 리스트 입니다.")
});
}결과
function home(){
const homeName = 'my House';
homeName = 'your house';
console.log(homeName);
}
home();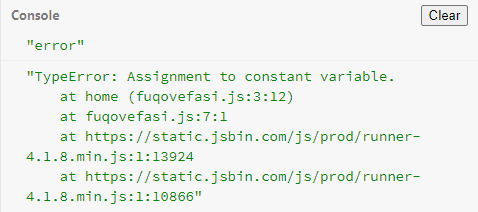
const를 사용하더라도 배열과 오브젝트의 값을 변겅하는 것은 가능하다.
즉, 값을 재할당하는 코드만 제한되는 것이다.
function home(){
const homeList = ['A','B','C'];
homeList.push("D");
console.log(homeList);
}
home();
immutable Array - 복사
function home(){
const homeList = ['A','B','C'];
homeList2 = [].concat(homeList , "D");
console.log(homeList === homeList2); //결과 false
}
home();
결론
const를 기본적으로 사용하며 변경이 될 수 있는 변수는 let을 사용하자.
또한 var 는 사용하지 않는다.